Earths Crust
Outer Layer of Earth
The Earths crust is the outermost layer of the Earth. It is covered with continental crust and oceanic crust. Rising plumes of heat from the Earth's core cause the plates to move. The convection currents cause the plates to collide and move apart. Other plates move horizontally past another plate. All plate movement at these boundaries cause both large and small earthquakes.
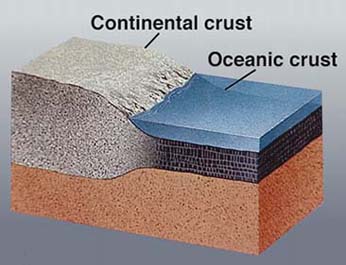
Continental crust
Continental crust is much older than oceanic crust. The basement rocks of the continents are granitic rocks. Granitic rocks are lighter than oceanic crust rocks. The minerals that make up the crust are primarily quartz and feldspar.
When two crustal plates meet the continental crust is never destroyed. Instead, it overrides oceanic crust or smashes together with another continental crust to form great mountain chains. The Himalaya Mountains are growing as the Eurasian Plate collides with the Indian Plate and the Earths crust is not destroyed.
Rocks on ocean floors
Oceanic crust is formed from periodite in the upper mantle. When this lava flows out on the ocean floors it forms pillow basalt. Basalt is an iron rich igneous rock made of magnetite, hornblende and other heavy minerals. The basalt flowing out of vents forms pillow basalt that covers all the ocean floors.
Sediment from the continent flows into the oceans and covers the ocean floor with silt and other rock debris. As the layers of sediment deepen they cover the pillow basalt with sedimentary rock.
Density of Earth's plates
The density of oceanic plates are approximately 3.3 grams per cubic centimeter. Continental crust is only 2.7 grams per cubic centimeter. When these two different types of plates meet the oceanic plate bends and begins to slip underneath the lighter continental plate forming a trench between the plates where they meet.
Density is why the continental crust always overrides the heavier oceanic crust. The oceanic crust melts as it forced downward beneath the continental crust. The rocks are recycled and form new igneous rocks when volcanoes erupt.
More Facts About Earth Links
KIDS FUN SCIENCE BOOKSTORE
 |
 |
Check out Myrna Martin's award winning textbooks, e-books, videos and rock sets. The Kids Fun Science Bookstore covers a wide range of earth science topics. Click here to browse.
Sign up to our monthly newsletter and receive our FREE eBook containing 3 fun activities that don’t appear in any of our other books!
The Kids Fun Science monthly newsletter will include the following: current events, weird and fantastic facts, a question of the month, science trivia and the latest new content from our website.
We respect your privacy and you can be assured that we will never share your email address or use it for any other purpose than to send you our newsletter.






